Have you ever wondered what security analysts actually do? Buckle up, because we’re diving into a thrilling investigation of a malware attack! Today’s culprit? The notorious Pushdo trojan.
This post will take you through a simulated security assessment, mimicking the thought process and steps involved in uncovering malicious activity. We’ll dissect alerts, explore the tools used for analysis, and ultimately expose the tricks employed by Pushdo.
So, grab a cup of coffee (or your beverage of choice), and let’s embark on this malware takedown adventure!
CyberOps Associates v1.0 - Skills Assessment
Introduction
You have been hired as a junior security analyst. As part of your training, you were tasked to determine any malicious activity associated with the Pushdo trojan.
You will have access to the internet to learn more about the events. You can use websites, such as VirusTotal, to upload and verify threat existence.
The tasks below are designed to provide some guidance through the analysis process.
You will practice and be assessed on the following skills:
- Evaluate event alerts using Squil and Kibana.
- Use Google search as a tool to obtain intelligence on a potential exploit.
- Use VirusTotal to upload and verify threat existence.
Content for this assessment was obtained from http://www.malware-traffic-analysis.net/ and is used with permission. We are grateful for the use of this material.
Required Resources
- Host computer with at least 8GB of RAM and 45GB of free disk space
- Latest version of Oracle VirtualBox
- Security Onion virtual machine requires 4GB of RAM using 25GB disk space
- Internet access
Instructions
Part 1: Gather the Basic Information
In this part, you will review the alerts listed in Security Onion VM and gather basic information for the interested time frame.
Step 1: Verify the status of services
a. Log into Security Onion VM using with the username analyst and password cyberops.
b. Open a terminal window. Enter the sudo so-status command to verify that all the services are ready.
Right-click on the desktop background and select “Open Terminal”.
analyst@SecOnion:~$ sudo so-status
Status: securityonion
* sguil server [ OK ]
Status: seconion-import
* pcap_agent (sguil) [ OK ]
* snort_agent-1 (sguil) [ OK ]
* barnyard2-1 (spooler, unified2 format) [ OK ]
Status: Elastic stack
* so-elasticsearch [ OK ]
* so-logstash [ OK ]
* so-kibana [ OK ]
* so-freqserver [ OK ]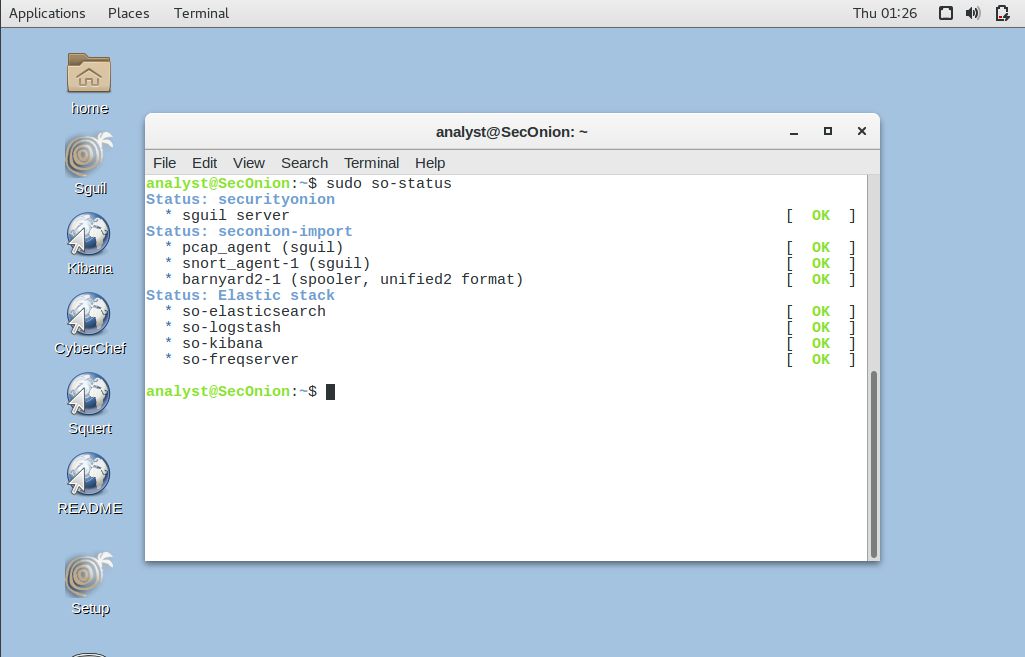
c. When the nsm service is ready, log into Sguil or Kibana with the username analyst and password cyberops.
Open Sguil using the shortcut on the desktop. Log in with the username “analyst” and the password “cyberops”. Click “Select All” to select the interfaces, and then click “Start SGUIL”.
Step 2: Gather basic information.
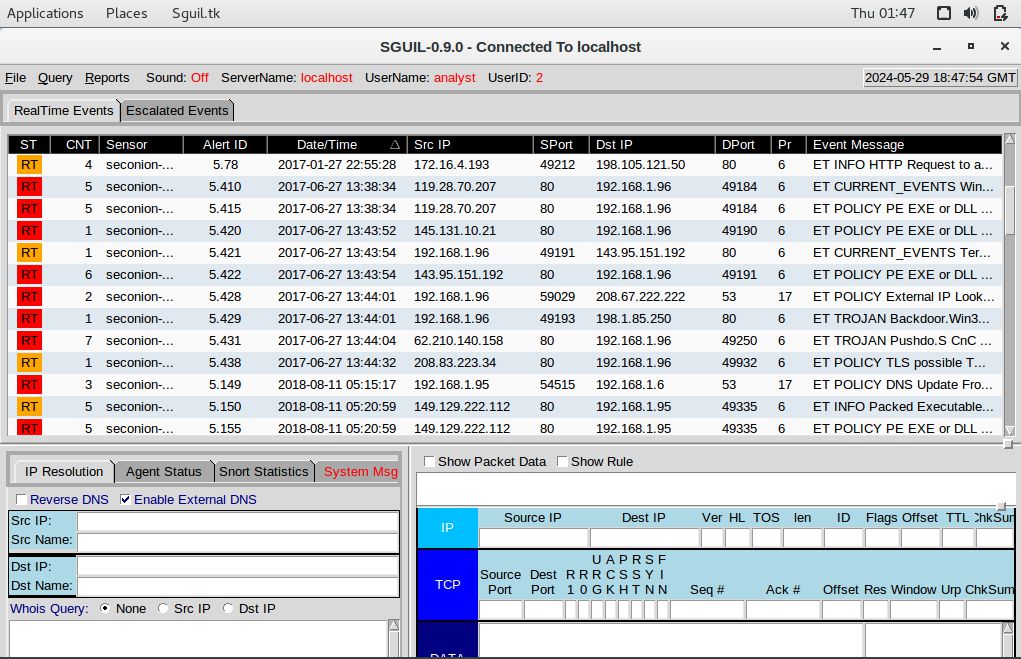
a. Identify time frame of the Pushdo trojan attack, including the date and approximate time.
2017-06-27 from 13:38:34 to 13:44:32b. List the alerts noted during this time frame associated with the trojan.
ET CURRENT_EVENTS WinHttpRequest Downloading EXE
ET POLICY PE EXE or DLL Windows file download HTTP
ET POLICY PE EXE or DLL Windows file download HTTP
ET CURRENT_EVENTS Terse alphanumeric executable downloader high likelihood of being hostile
ET POLICY PE EXE or DLL Windows file download HTTP
ET POLICY External IP Lookup Domain (myip.opendns .com in DNS lookup)
ET TROJAN Backdoor.Win32.Pushdo.s Checkin
ET TROJAN Pushdo.S CnC response
ET POLICY TLS possible TOR SSL trafficc. List the internal IP addresses and external IP addresses involved.
Internal IP Address:
- 192.168.1.96
External IP Addresses:
- 143.95.151.192
- 119.28.70.207
- 145.131.10.21
- 62.210.140.158
- 119.28.70.207
- 208.67.222.222
- 208.83.223.34
- 198.1.85.250Part 2: Learn about the Exploit
In this part, you will learn more about the exploit.
Step 1: Infected host
a. Based on the alerts, what is the IP and MAC addresses of the infected computer? Based on the MAC address, what is the vendor of the NIC chipset? (Hint: NetworkMiner or internet search)
Right-click Alert ID: 5410 and select NetworkMiner
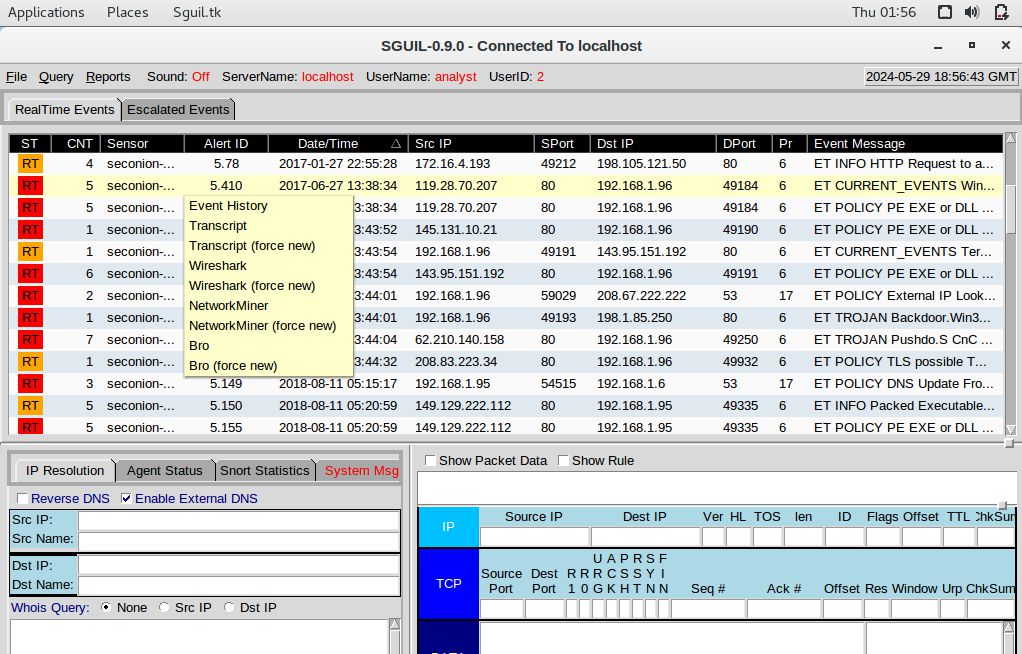
Based on the alerts, here are the requested details:
IP: 192.168.1.96
MAC: 00-15-C5-DE-C7-3B
NIC Vendor: Dell Inc.b. Based on the alerts, when (date and time in UTC) and how was the PC infected? (Hint: Enter the command date in the terminal to determine the time zone for the displayed time)
On NetworkMiner windows, click Files tab to determine date and time in UTC:
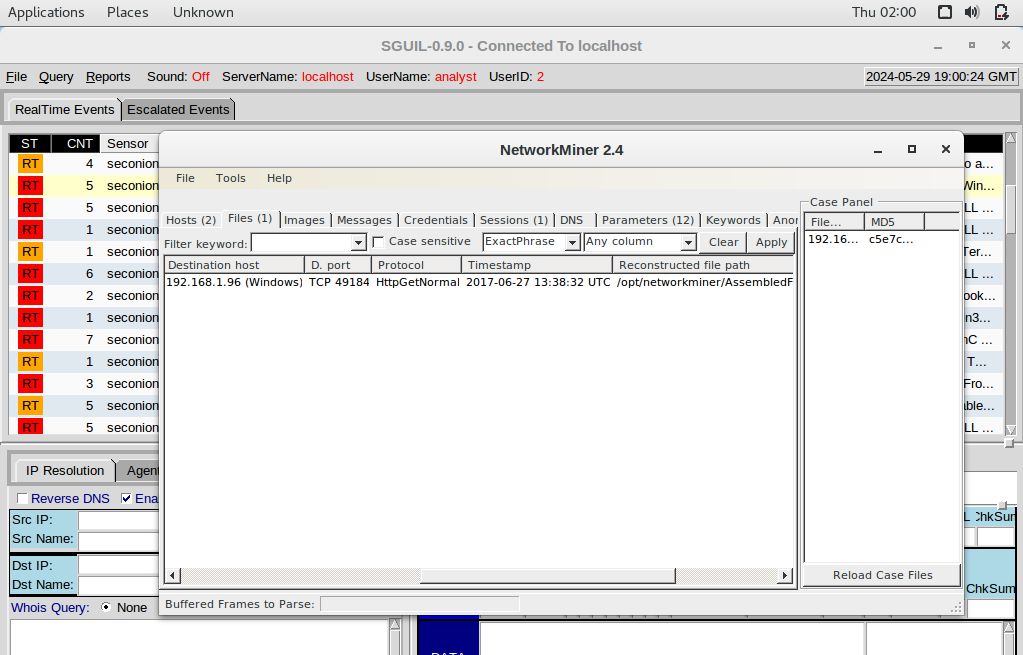
Based on the alerts, here are the requested details:
2017-06-27 13:38:32 UTC
The gerv.gun malware was executed through the Pushdo trojan.How did the malware infect the PC? Use an internet search as necessary.
The user on the PC with the IP address 192.168.1.96 inadvertently accessed a malicious website, resulting in the installation of the Pushdo trojan. Pushdo operates as a “downloader” trojan, meaning its main function is to download and install additional malicious software onto the infected system. Upon execution, Pushdo communicates with various control server IP addresses embedded within its code. These servers typically masquerade as Apache web servers and listen on TCP port 80. When specific parameters are present in the HTTP request, Pushdo delivers one or more executable files via HTTP. The type of malware downloaded by Pushdo is determined by the value following the “s-underscore” part of the URL.
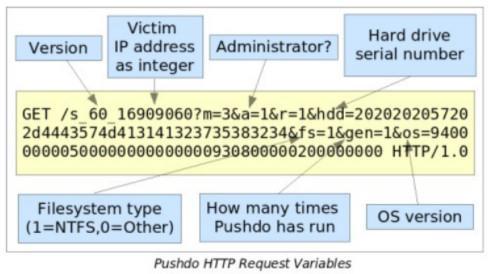
Pushdo gathers various information from the victim’s system, including their IP address, administrative privileges status, primary hard drive serial number obtained through SMART_RCV_DRIVE_DATA IO control code, file system type (typically NTFS), the number of times a Pushdo variant has been executed on the system, and the version of Windows operating system retrieved through the GetVersionEx API call.
Step 2: Examine the exploit.
a. Based on the alerts associated with HTTP GET request, what files were downloaded? List the malicious domains observed and the files downloaded.
Right-click Alert ID: 5410, then select Transcript
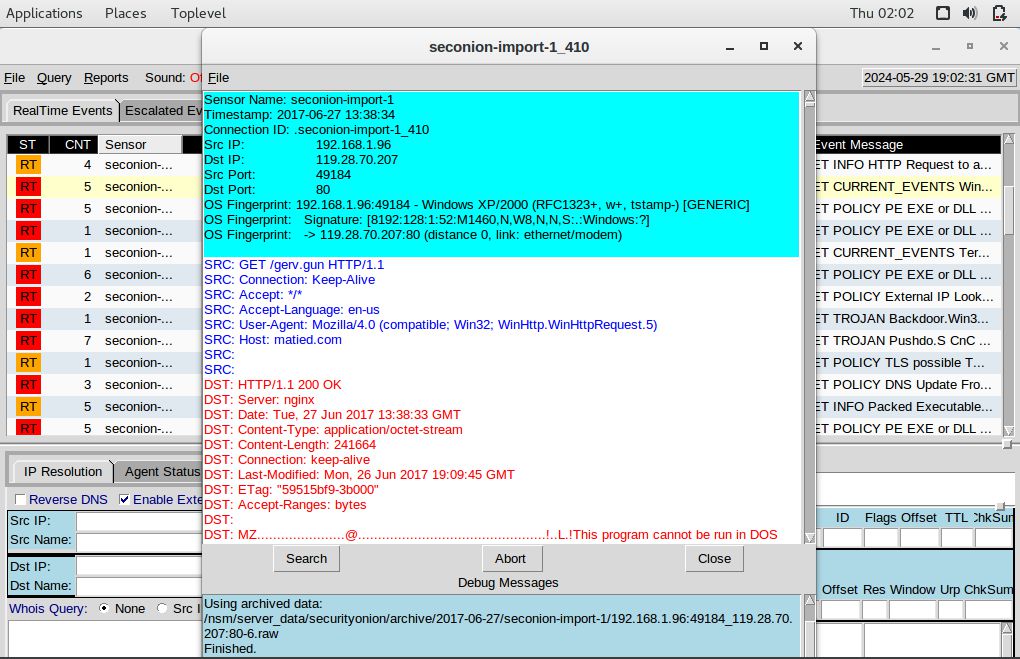
Right-click Alert ID: 5420, then select Transcript
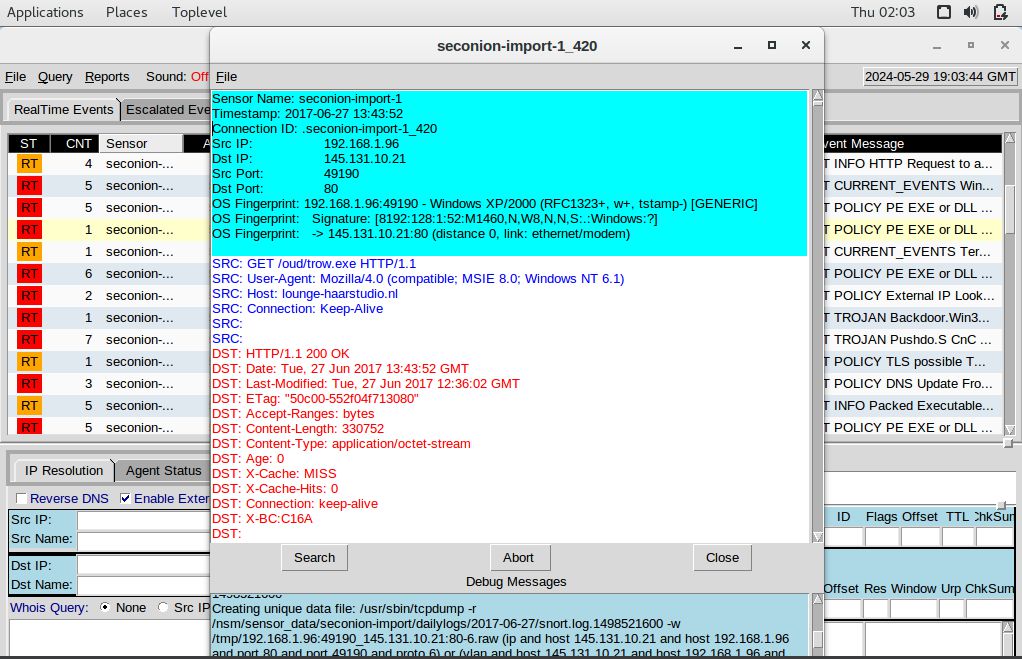
Right-click Alert ID: 5421, then select Transcript
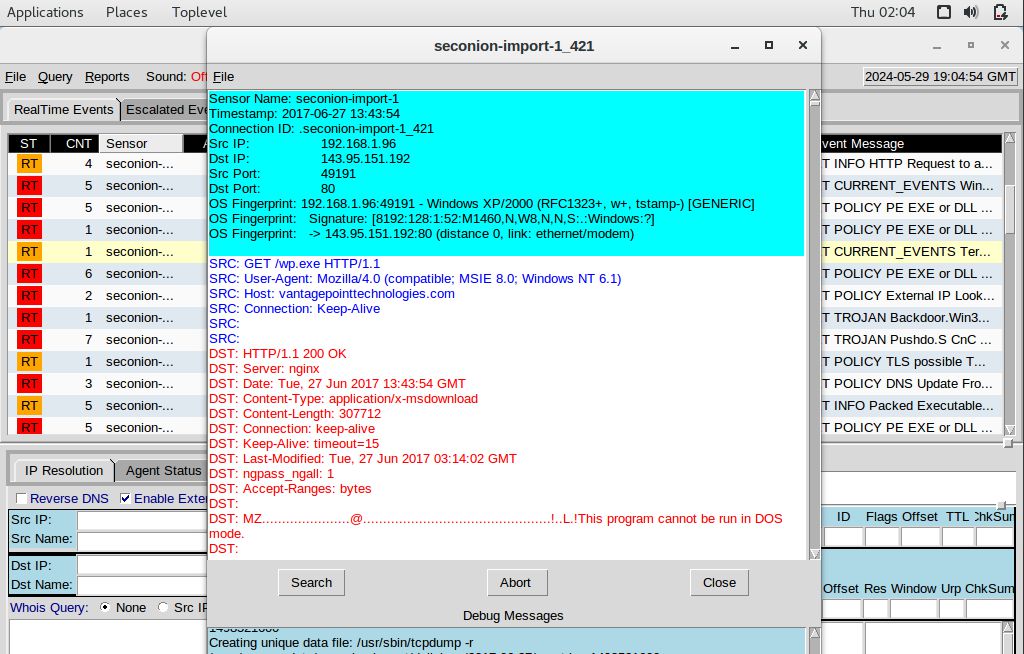
Based on the alerts, here are the requested details:
gerv.gun – matied.com/gerv.gun
trow.exe – lounge-haarstudio.nl/oud/trow.exe
wp.exe – vantagepointtechnologies.com/wp.exeUse any available tools in Security Onion VM, determine and record the SHA256 hash for the downloaded files that probably infected the computer?
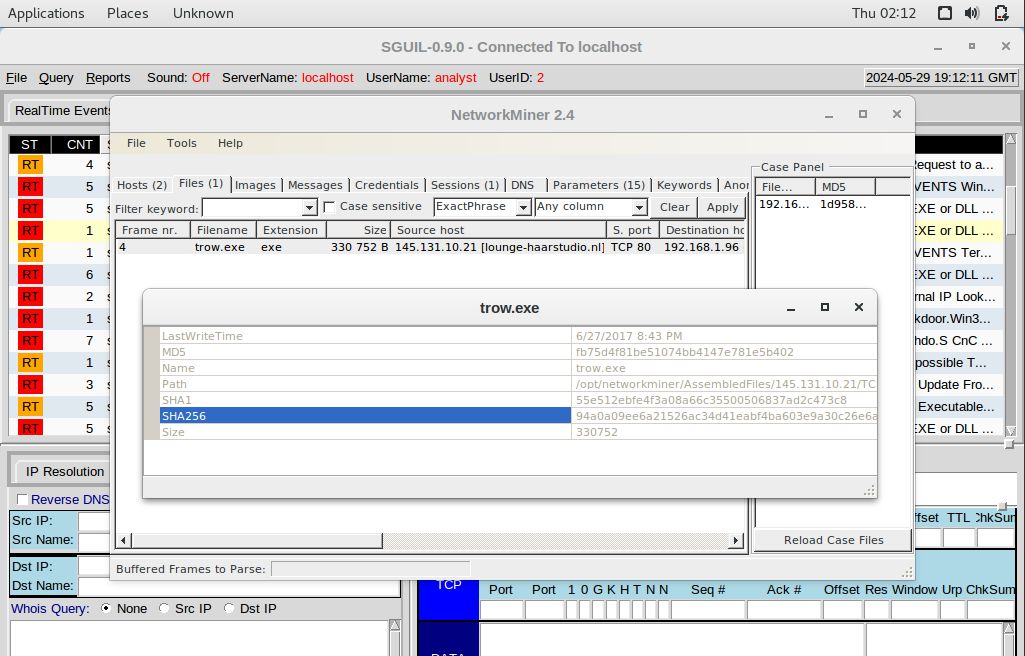
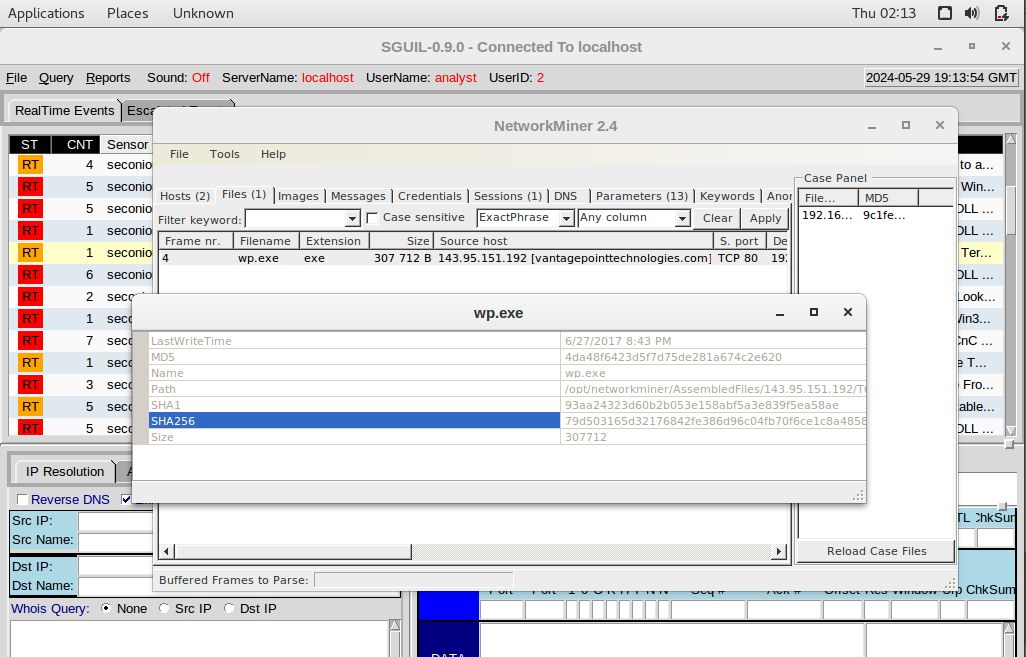
Utilize the NetworkMiner tool in the following manner: Right-click Alert ID: 5410, choose NetworkMiner, then navigate to the Files tab. Right-click on the first line and select Calculate MD5 / SHA1 / SHA256 hash.
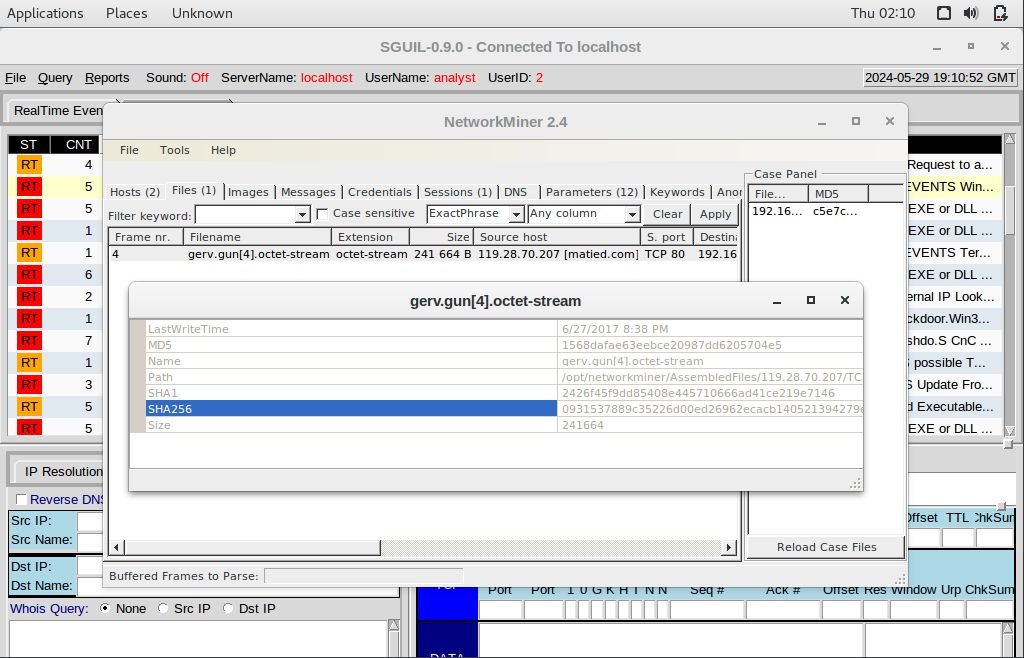
Provide the SHA256 hash for the files trow.exe and wp.exe corresponding to Alert IDs 5420 and 5421.
Based on the results, here are the requested details:
gerv.gun = 0931537889c35226d00ed26962ecacb140521394279eb2ade7e9d2afcf1a7272
trow.exe = 94a0a09ee6a21526ac34d41eabf4ba603e9a30c26e6a1dc072ff45749dfb1fe1
wp.exe = 79d503165d32176842fe386d96c04fb70f6ce1c8a485837957849297e625ea48b. Navigate to www.virustotal.com input the SHA256 hash to determine if these were detected as malicious files. Record your findings, such as file type and size, other names, and target machine. You can also include any information that is provided by the community posted in VirusTotal.
Open the Chromium web browser, navigate to www.virustotal.com, click on “Search” tab and enter the hash.
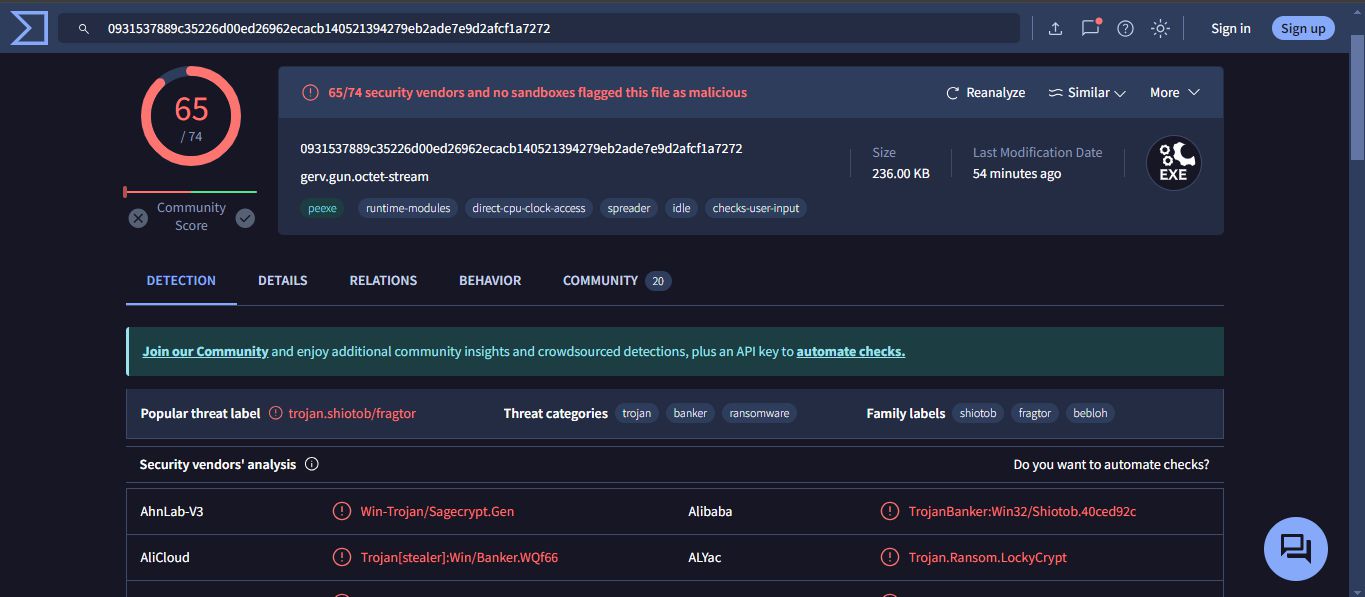
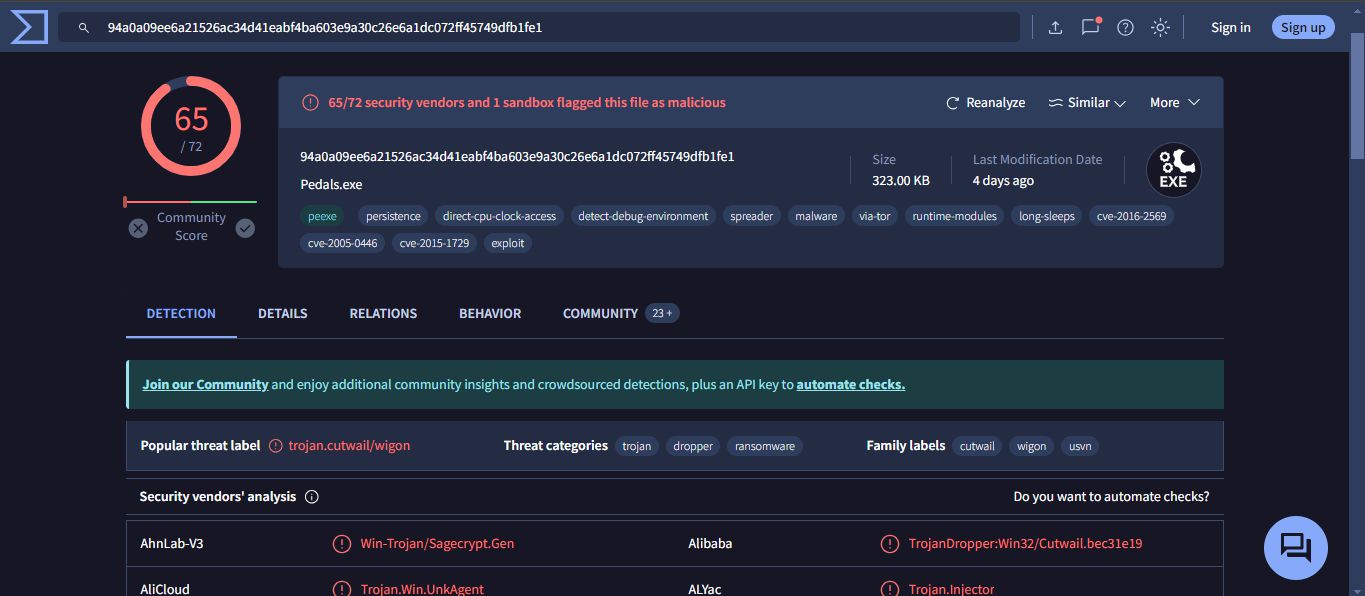
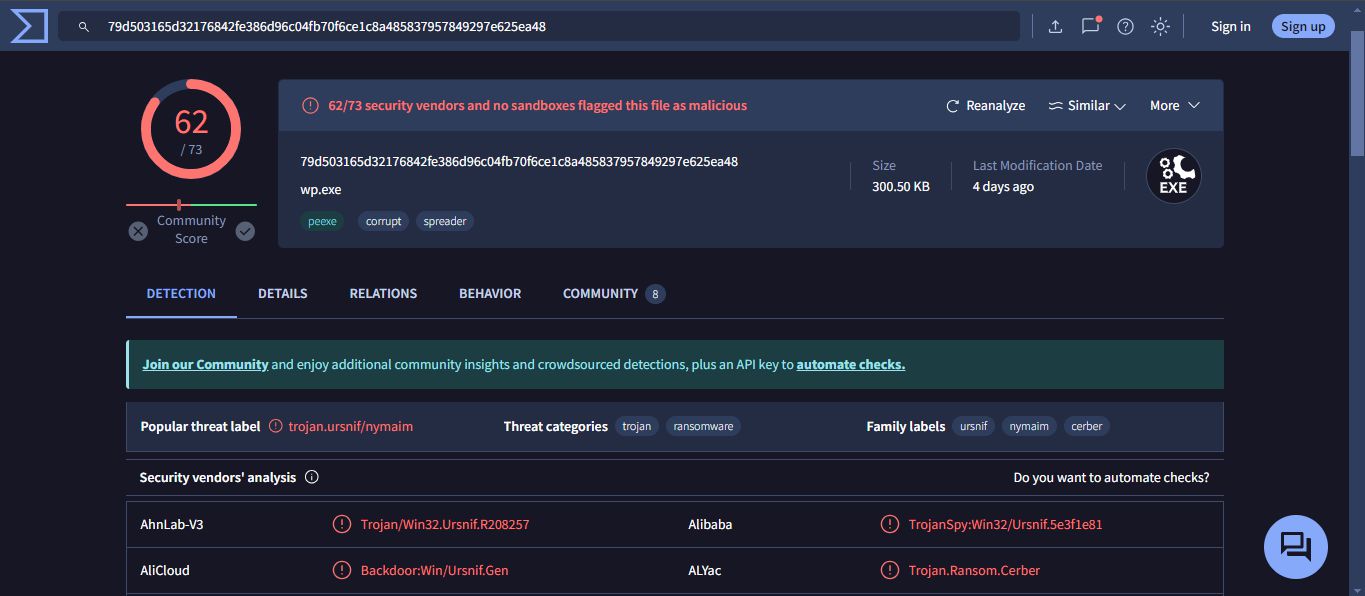
Based on the results, here are the requested details:
| File Name | Engines Detected | File Type | File Size | Alternate Names | Target Machine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gerv.gun | 65 | Win32 EXE | 236.00 KB (241664 bytes) | gerv.gun.octet-stream, gerv.gun[11].octet-stream, gerv.gun[12].octet-stream, gerv.gun[8].octet-stream, gerv.gun[6].octet-stream, gerv.gun.exe, (5.410) gerv.gun.octet-stream, gerv.gun, gerv.zip, gerv (1).gun, gerv.gun.bin, img (1), grun.exe, gerv.exe, gerv.gun[1].octet-stream, gerv.gun[2].octet-stream, gerv.gun[5].octet-stream, gerv.gun[9].octet-stream, gerv.gun[3].octet-stream, HTTP-FG0jno3bJLiIzR4hrh.exe, test, tmp523799.697, tmp246975.343, tmp213582.420, extract-1498570714.111294-HTTP-FG0jno3bJLiIzR4hrh.exe, 0931537889c35226d00ed26962ecacb140521394279eb2ade7e9d2afcf1a7272.bin, vector.tui | Intel 386 or later processors and compatible processors |
| trow.exe | 65 | Win32 EXE | 323.00 KB (330752 bytes) | trow.exe, trow[1].exe, Pedals, Pedals.exe, trow[5].exe, suspect file1, trowexecutablepotential, suspect executables, Suspect Executables, trow, steam 0.0, 0.0 trow.exe, http0, steam5.5, steam 4.4, trow.html, suspect 2, Trow, throw2.exe, taswexuahoft.exe, trow.http, trow1(1).exe, trow(3).exe, MalwareDownload, trow.dat, trow(1).exe, trow[2].exe, HTTP-FfmePA13Dx2LcgCLd.exe, trow.bin, bad, test3, 2017-06-28_18-18-14.exe, bma2beo4.exe | Intel 386 or later processors and compatible processors |
| wp.exe | 62 | Win32 EXE | 300.50 KB (307712 bytes) | wp.exe, wp[5].exe, binck.exe, wp(1).exe, suspect file 2, wpExecutablepotential1, wp[1].exe, suspect executables 2, wp[2].exe, Suspect Executables1, wp, wp.exe1, wp.exe.bin, trow.exe, suspect 1, wp.http, wp.dat, wp[4].exe, HTTP-FiS6Ty18r3jnk9xajj.exe, malware, test2, wp.bin, wp.exe.x-msdownload, 4da48f6423d5f7d75de281a674c2e620.virobj, test_3 | Intel 386 or later processors and compatible processors |
c. Examine other alerts associated with the infected host during this timeframe and record your findings
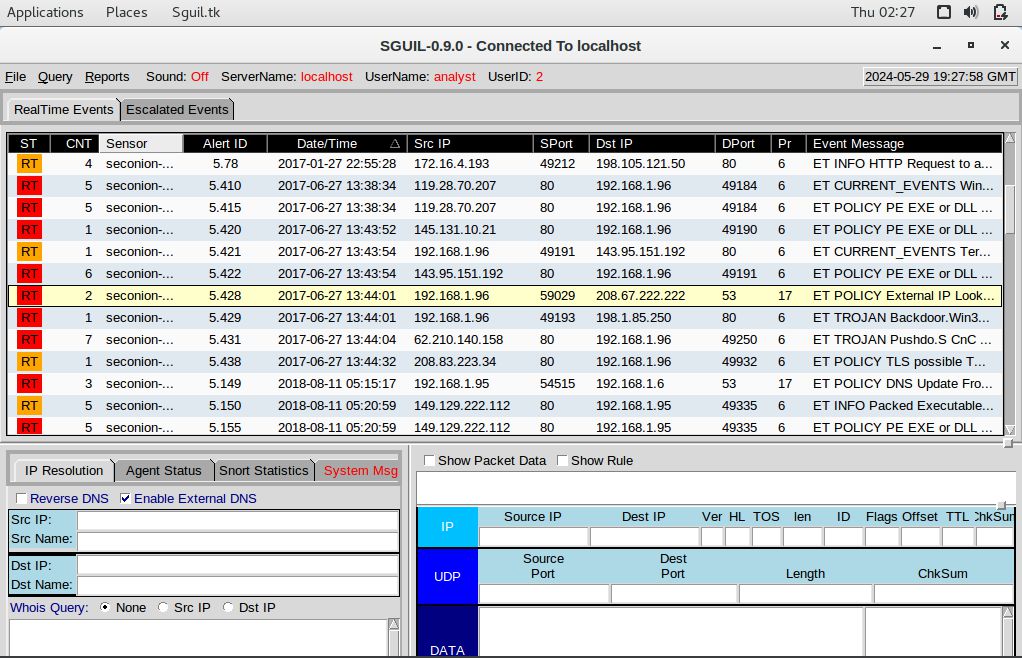
Based on the alerts, here are the requested details:
ET POLICY External IP Lookup Domain (myip.opendns.com in DNS lookup)
The infection started when the user of the 192.168.1.96 host performed a DNS lookup through a malicious domain.
The destination IP was 208.67.222.222Step 3: Report Your Findings
Summarizes your findings based on the information you have gathered from the previous parts, summarize your findings.
A PC with IP address 192.168.1.96, running Windows, was compromised after accessing a malicious domain via a DNS query. The Pushdo trojan infected the system, disguising itself as an Apache web server by listening on port 80, making detection difficult. Once inside, Pushdo downloaded and installed additional malware: gerv.gun, trow.exe, and wp.exe. These files were confirmed as malicious through VirusTotal analysis, which showed detection by multiple antivirus engines. This incident emphasizes the importance of strong cybersecurity measures, including monitoring DNS activity and promptly addressing security anomalies.